
In drug development and clinical research, data standardization is the cornerstone of ensuring reproducible results, traceability, and compliance with regulatory review requirements. SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model), ADaM (Analysis Data Model), and Define.XML—defined by CDISC (Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium)—form a comprehensive technical framework spanning raw data collection to final statistical analysis. This article explores their critical roles and includes key diagrams to enhance understanding and application.
1. Mandatory Data Standards
Studies initiated after December 17, 2016 must adopt unified data standards (e.g., CDISC standards) to enable efficient FDA review via standardized tools.
Studies initiated before 2016 are strongly advised to follow these standards to improve data compatibility.
2. Unified Review Platform
A centralized submission platform supports structured integration of trial data (e.g., SDTM/ADaM formats) across the clinical trial lifecycle.
Addresses challenges in reviewing non-standardized data (e.g., manual forms, unstructured text), reducing regulatory risks.
Process Flexibility: Allows dynamic adjustments to study protocols or eCRFs during trials, minimizing delays from design changes.
Efficient Submission: Standardized formats shorten submission and FDA review cycles (e.g., fewer repetitive queries).
Cost Optimization: Reduces redundant development costs through predefined trial components (e.g., common endpoints, statistical methods).
Scientific Rigor: Standardized data enable cross-study meta-analysis, accelerating discoveries.
Regulatory Trust: Unified standards enhance FDA confidence in data integrity, lowering rejection risks due to quality issues.
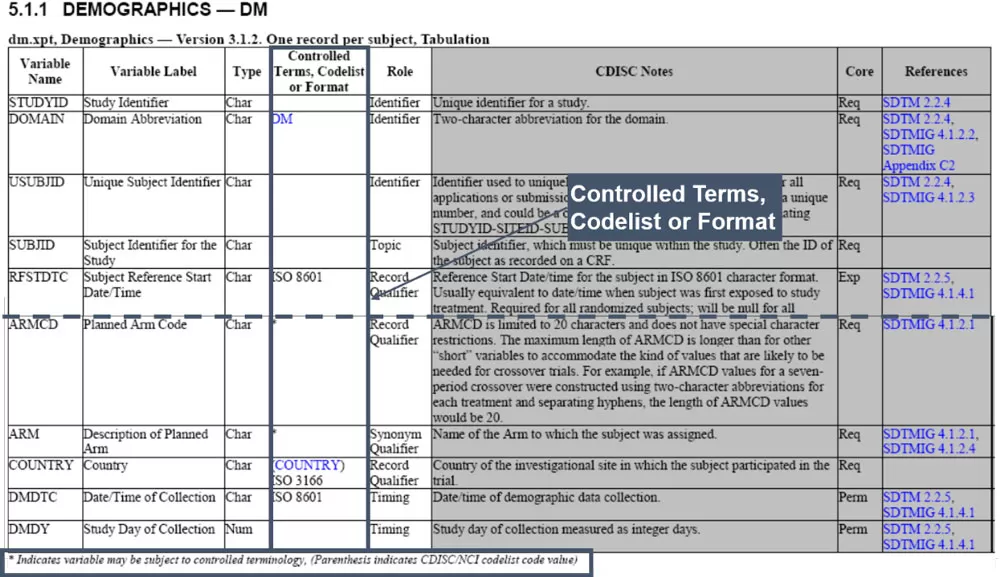
SDTM is a standardized representation model for raw clinical trial data. By leveraging predefined domains and variables, it simplifies complex issues and clarifies ambiguous logic.
Definition: A discrete unit of information collected in a clinical trial.
Example: "Subject 101 experienced mild nausea on Study Day 6."
Definition: A collection of observations organized around a common theme.
Examples: Adverse Events (AE), Demographics (DM).
Definition: Structured data attributes constituting an observation.
Examples: Subject ID (USUBJID), Event Name (AETERM), Start Date (AESTDTC).
1. Grouping Qualifiers: Classify observations across subjects or within a subject (e.g., treatment group, demographics).
2. Result Qualifiers: Capture raw or standardized results in "findings" domains (e.g., lab test values).
3. Synonym Qualifiers: Provide alternative names for variables (e.g., mapping local terms to CDISC terminology).
4. Record Qualifiers: Describe overall properties of observations (e.g., subject posture during vital signs, AE severity).
5. Variable Qualifiers: Supplement variable values (e.g., units –STRESU, normal ranges –NRIND).
Variable Length: Ensure character variables comply with standards (e.g., XXTEST ≤40 characters, XXTESTCD ≤8 characters).
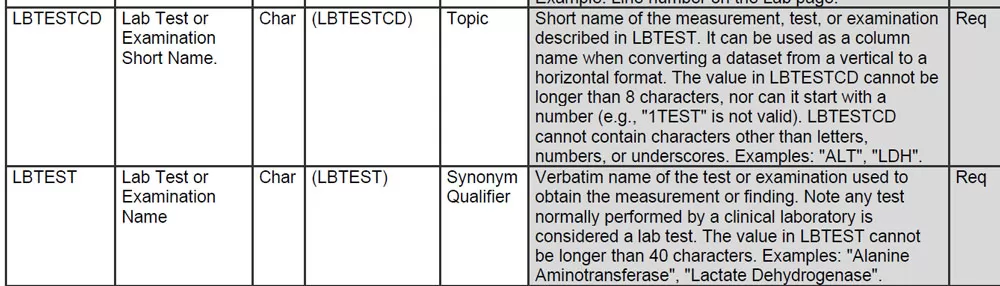
Time Variable Format: Use ISO 8601 (e.g., 2024-07-21T08:30).
Collected | Dec 15, 2003, 1:14:17 PM | Dec 15, 2003, 1:20 PM | Dec 15, 2003 | Dec 200 | 2003 |
Not Known or Collecte | - | Seconds | Time | Day, Tim | Month, Day, Time |
--DTC Value | 2003-12-15T13:14:17 | 2003-12-15T13:20 | 2003-12-15 | 2003-12 | 2003 |
Controlled Terminology: In the SDTMIG (SDTM Implementation Guide), many variables are subject to controlled terminology requirements:
Use tools like Pinnacle 21 to validate compliance with CDISC terminology standards, and regularly download the latest terminology files from the CDISC website.
ADaM is designed to support clear and unambiguous communication in statistical analysis by providing datasets that are both comprehensible and traceable.
Quality: Ensure clear statistical communication through dataset structure and content.
Traceability: Enhance understanding of data lineage from source to analysis.
Efficiency: Provide analysis-ready datasets to accelerate result generation and review.
Metadata: Supply metadata for datasets, variables, parameters, and results, along with methodological and statistical details.
Submission: Meet requirements from regulatory agencies (e.g., FDA) for standardized analysis datasets.
1. Minimal Preprocessing
Datasets are structured to allow analysts to reproduce statistical conclusions without complex operations.
2. Eliminate Redundant Variables
Retain only variables directly relevant to statistical analysis to reduce confusion. For example, omit variables that can be derived from existing fields.
3. One-Step Analysis
Design datasets to produce statistical results through a single analytical step, such as pre-calculated variables like baseline (BASE), change from baseline (CHG), or standardized analysis variables (e.g., AVAL).
4. Reduce Reviewer Burden
Utilize standardized variable naming, logical annotations, and embedded metadata to enable regulatory reviewers to verify results without additional programming.
Metadata serves as a tool to clearly and succinctly convey analysis results from Contract Research Organizations (CROs) to sponsors and regulatory reviewers, encompassing the following components:
Statistical Methods: Documentation of analytical approaches.
Data Transformations: Steps applied to raw data (e.g., normalization, aggregation).
Assumptions: Key assumptions underlying the analysis (e.g., missing data handling).
Derivations and Imputations: Rules for calculated variables or imputed values.
Machine-Readable Format: CDISC mandates metadata to be in machine-readable formats (e.g., XML) to facilitate the development of standardized analytical tools.
1. Statistical Analysis Plan (SAP)
Describes statistical methods, defines assumptions, and specifies rules for missing data imputation and derivations.
2. Analysis Dataset Specification (ADS)
Documents data transformation processes, defines algorithmic logic (e.g., complex calculation rules), and includes metadata for datasets and variables (e.g., code lists used).
3. SAS Datasets
Store actual data details such as final variable lengths and enforced code values.
Integration via ADRG: All metadata is consolidated through the Analysis Data Reviewers Guide (ADRG) and mapped to the define.xml file for structured linkage.
1. Metadata Traceability
Ensure transparent mapping between analysis datasets and source data (e.g., SDTM domains).
Document variable definitions, algorithmic logic, and data cleaning rules.
2. Data Point Traceability
Support reverse tracing from analysis results back to raw observations.
Enable cross-dataset linkage via identifiers (e.g., USUBJID, ASEQ).
These mechanisms collectively ensure that the statistical logic and scientific conclusions of the study are communicated clearly and unambiguously to regulatory agencies and collaborating teams.
Define.XML is a metadata descriptor file for SDTM/ADaM datasets, containing the following sections:
1.Supplementary Files and Datasets
This section includes auxiliary files to enhance the understanding and interpretation of submitted data.
Reviewers can click on the dataset name in the left panel to directly navigate to the corresponding detailed description table.

2. Controlled Terminology: Due to challenges in maintaining uniform data collection standards across different clinical trials, raw data values often vary. To address this, CDISC has standardized the values of specific data points. This module in the Define file is used to present the harmonized submission values for these standardized data points.
3. Variable Derivation Methods: This section in the Define file acts as a "dictionary" for derivation logic. All variable derivation methods mentioned in the dataset description modules are cataloged here. This allows reviewers to verify the correctness and rationale of computational processes, ensuring the reliability of analysis results.


End-to-End Standardization: SDTM → ADaM → Define-XML forms a complete data pipeline, spanning the entire lifecycle from data collection, analysis, to regulatory submission.
Efficient Review: By linking SDTM and ADaM metadata, Define.XML significantly reduces regulatory queries on data logic, accelerating the review process.
Reusability: Standardized data and metadata enable cross-trial, cross-sponsor data pool integration and analysis (e.g., meta-analysis).
SDTM, ADaM, and Define.XML are the three pillars of data standardization in drug development. They not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also enhance scientific rigor and operational efficiency. A compliant data standardization process reduces submission preparation timelines while ensuring the credibility and reproducibility of study results.
SAS: Industry-standard software for SDTM/ADaM implementation.
Pinnacle 21 Community: Validates SDTM/ADaM compliance and generates Define.XML.
Next Steps: Not Sure if Your ADam, SDTM, or Define.xml is Submission Ready?
Our team of biometrics experts offers complimentary consultations. We'll assess your protocol, analysis plan, data quality, biometrics resources, and vendor gaps—at no cost.
Contact: Suling Zhang, VP of International Operations and Business Development
Email: suling.zhang@gcp-clinplus.com
Phone: +1 609-255-3581
With 22 years of experience, 2,200+ successful projects, and 160+ NDA approvals from FDA, NMPA, and EMA, GCP ClinPlus offers unparalleled biometrics expertise. Our US team brings 30+ years of global regulatory experience to every engagement.