As clinical trials step into the digital age, data governance has become a core element in ensuring trial quality. By introducing a completely new [Data Governance] chapter, GCP 2025 establishes systematic regulations for electronic data management and the maintenance of blinding. This marks the formal and comprehensive alignment of China's drug clinical trial regulatory system with the digital era. Today, we deconstruct the core changes within this new chapter.
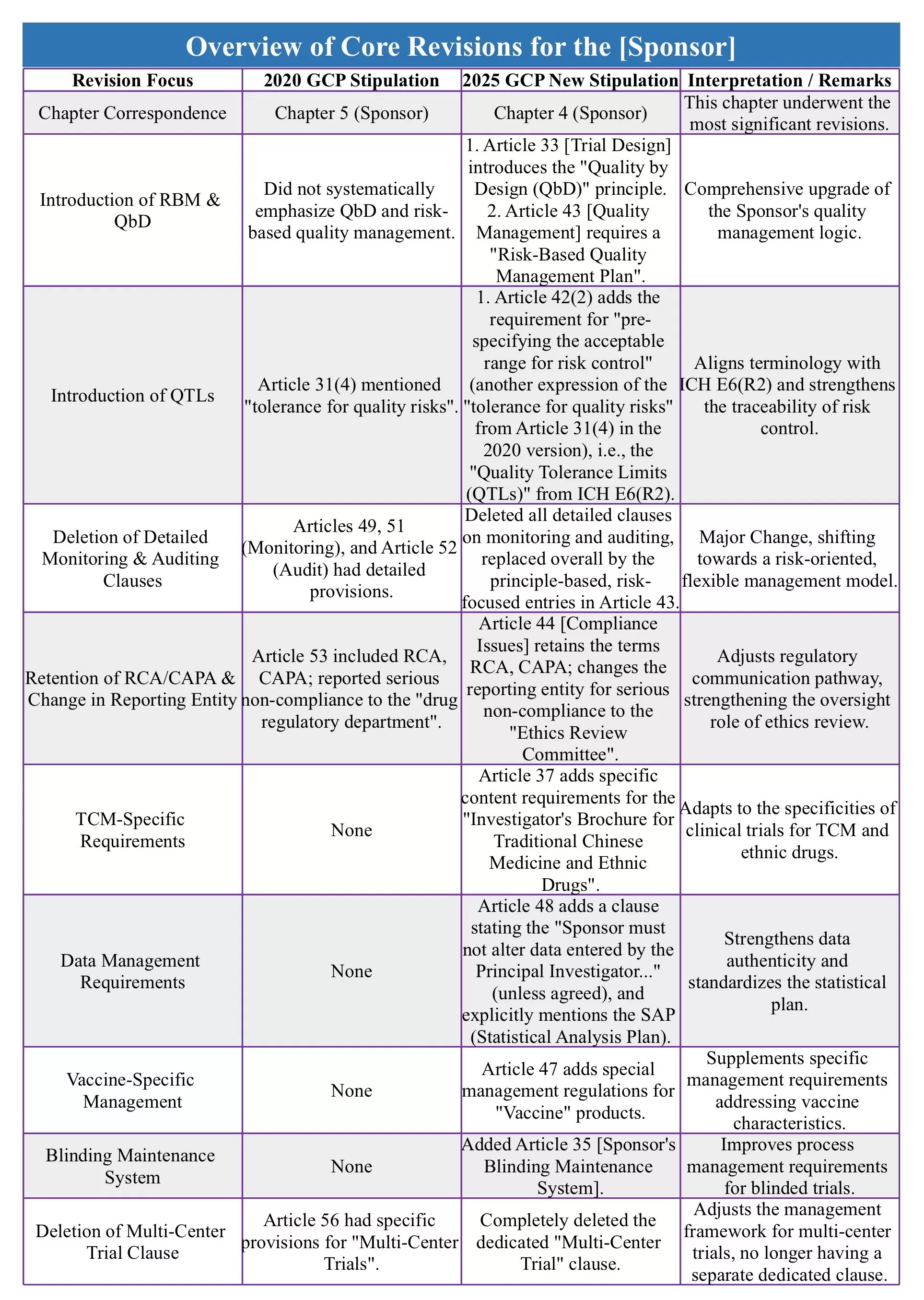
The establishment of an independent Data Governance chapter is a crucial step in the modernisation of the GCP. This chapter systematically integrates data management requirements that were previously scattered across various sections, building a management system that covers the entire data lifecycle. This transformation is not only a proactive response to digitalised clinical trials but also elevates "Data Quality" to an unprecedented strategic level.
These revisions both align with international regulatory trends and fully consider the practical needs of the digital development of clinical trials in China. By establishing a systematic data governance framework, it provides clear regulatory basis for electronic data management and blinding maintenance, and more importantly, signifies a fundamental shift in the regulatory mindset from process control to "Quality by Design".
The final installment tomorrow will focus on the major adjustments to the overall GCP framework, analysing the regulatory logic behind the streamlined chapter structure and how the core requirements from omitted chapters have been integrated into the new system. Stay tuned!